OEE Key Figure – Guide
A Comprehensive Insight into Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Introduction and Meaning
More than ever, efficiency is critical in today’s industry. This means that optimising production processes and increasing efficiency can help companies to remain competitive and, based on this, achieve sustainable growth. One key figure that plays an important role in this context is OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness). In the following, the significance of the concept is explained and why it is important for companies to continuously record and evaluate the OEE key figure.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness is a metric that measures the efficiency of production equipment by taking into account the availability, performance, and quality of a plant or machine. It therefore provides a comprehensive view of production performance and is therefore a useful tool for consequently identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies in production . Based on the monitoring and analysis, companies can therefore easily take improvement measures in order to continuously optimize their production performance.
The OEE metric has established itself as the industry standard because it allows companies to evaluate their performance compared to other companies in the same industry. Subsequently, the knowledge of one’s own key figures can help companies to identify their strengths and weaknesses in relation to the production processes and finally make targeted improvements. As a result, there is increased productivity and reduced downtime. In addition, the competitive position will be consolidated and improved.
Definition and Basics
Definition of the OEE key figure
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness, german) is a key performance indicator (KPI) that evaluates the efficiency of a production plant. It combines the availability, performance and quality of a machine or plant to provide a comprehensive picture of production efficiency (the percentage of high-quality units actually produced in relation to the theoretically possible production). Consequently, OEE provides information on how and whether a plant is using its full capacity and potential potential.
As a result, a high value indicates that the production plant is operating efficiently and wastes little time and resources, while a low value indicates inefficiencies and problems in the production process that need to be addressed.
The Formula for Calculating Overall Equipment Effectivity
To calculate it, the three main components of plant efficiency are multiplied together: availability, performance and quality. Accordingly, the OEE formula for calculation is as follows:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
Each of these components is expressed as a percentage and has a value between 0 and 100%. The individual components are explained in more detail below:
Availability: Measures the amount of time a plant is actually available for production relative to the planned production time.
Performance: Measures how fast a plant is operating compared to its maximum possible speed.
Quality: Measures the proportion of high-quality units produced during the production period.
Details can be found in the section on the main components of the OEE.
Calculating the metric allows companies to rate their production efficiency on a scale from 0% (no production) to 100% (maximum efficiency). In practice, companies typically aim for an OEE of 85% or higher, with values below 65% considered below average. However, the OEE ratio alone may not cover all aspects of production output. Therefore, companies should always look at OEE in the context of other operational metrics and performance indicators in order to gain a comprehensive understanding of their production processes.
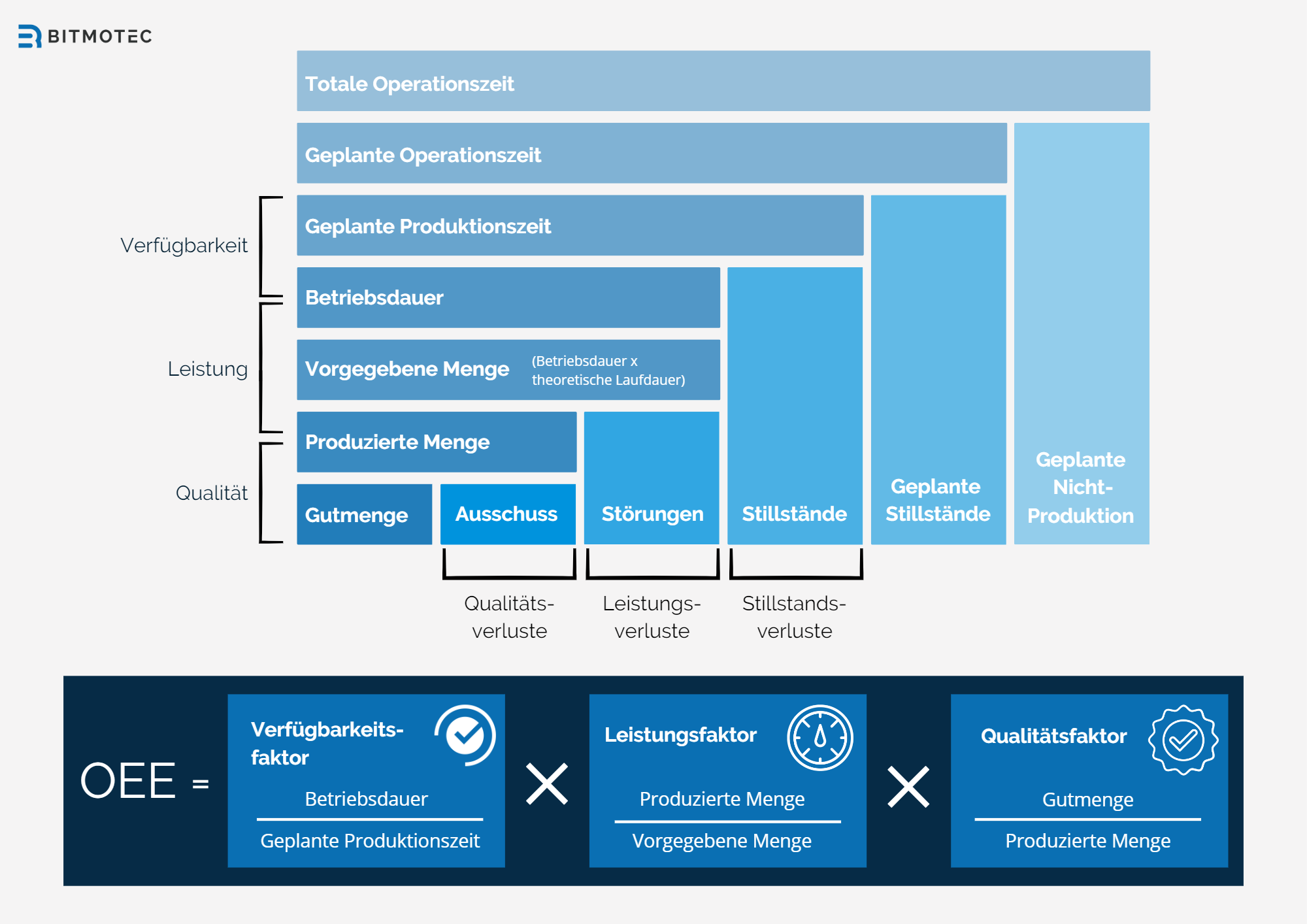
The three main components of OEE
- Availability (or machine availability or plant availability) is one of the main components of OEE and measures the time that a plant is actually available for production in relation to the planned production time.
- The performance factor, also known as the speed factor, measures the actual production speed of a plant compared to its maximum possible speed.
- The quality factor is the third major component of OEE and measures the proportion of high-quality units produced during the production period.
The combination of the three main components of availability, performance and quality makes it possible to calculate overall equipment effectiveness.
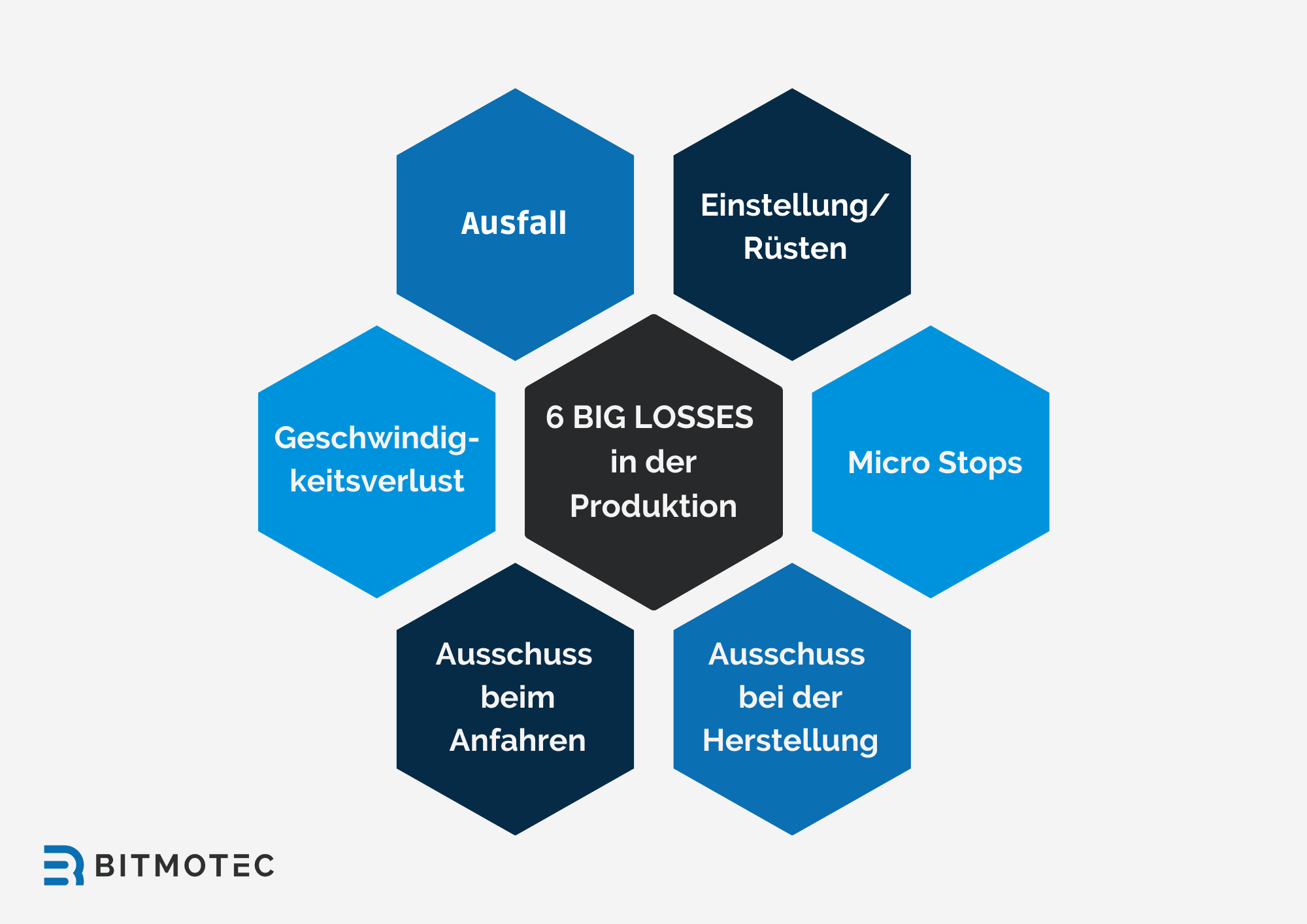
Causes of Efficiency Losses (Six Big Losses)
In OEE analysis, the so-called “Six Big Losses” are used to identify the main causes of efficiency losses in production. Accounting for these losses helps companies improve their OEE and optimize their production processes.
Breakdowns
Breakdowns are unplanned interruptions to production due to machine breakdowns, emergencies, or other unforeseen events. Outages lead to a reduction in availability and affect OEE. Through preventative maintenance and rapid response to failures, organizations can reduce downtime and increase overall equipment effectiveness.
Adjustment/Setup
Set-up and set-up times are planned interruptions in production caused by the change of products or tools, material preparation or machine settings. These times reduce availability and affect OEE. By optimizing set-up processes and applying methods such as SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die), companies can reduce set-up times and improve their overall equipment effectiveness.
Micro Stops
Micro stops are short, unplanned production interruptions caused by small disruptions or problems. They affect performance and OEE. Examples of micro stops are material jams, malfunctions of sensors or minor quality problems. By identifying and eliminating the root causes of micro stops, companies can increase their production speed.
Loss of speed
Loss of speed occurs when a plant operates slower than its maximum capacity. This affects performance and OEE. Loss of speed can be caused by inefficient work processes, lack of materials or inadequate machine settings. Companies can reduce speed losses by optimizing their processes and better aligning their equipment with production requirements.
Scrap at start-up
Start-up scrap refers to defective or low-quality products that arise during the start-up phase of production. This loss affects the Quality Score and OEE. To reduce start-up waste, companies can better prepare their equipment, optimize their processes, and train their employees.
Scrap during production
Manufacturing rejects are low-quality or defective products that are created during the regular production process. This loss affects the Quality Score and OEE. To reduce waste during manufacturing, companies should implement quality controls, constantly monitor their production processes, and make adjustments as needed. In addition, training and continuous improvement initiatives can help increase the quality of manufactured products.
Identifying and eliminating these six major losses allows companies to optimize their OEE and make their production processes more efficient. By continuously improving these areas, companies can increase their productivity, increase their product quality, and improve their competitiveness in the market.
The Benefits of OEE Measurement
OEE measurement and analysis offers many benefits to companies. By improving OEE, companies can optimize their production processes and achieve the following benefits:
Improved productivity and efficiency
Measuring OEE helps companies better understand their production processes and identify inefficiencies. By optimizing the OEE metric, companies can increase their production speed, use resources more efficiently, and increase productivity.
Reduction of downtime and production costs
Identifying weak points in production, such as machine breakdowns or long set-up times, allows companies to take steps to reduce this downtime. An improved OEE metric leads to less downtime and thus a reduction in production costs.
Improved product quality and customer satisfaction
OEE measurement helps to identify quality problems at an early stage and to initiate appropriate countermeasures. A higher OEE ratio often correlates with better product quality, which in turn can lead to higher customer satisfaction.
Overall, measuring OEE provides an opportunity for companies to continuously monitor and improve their production processes. By increasing the OEE ratio, companies can increase their competitiveness, increase their efficiency and be successful in the long term.
Implementing Overall Equipment Effectivness in Industrial Processes
Implementation in industrial processes is an important step in improving productivity and efficiency.
- Important considerations before implementation: Creating an understanding of current production processes, defining objectives and allocating sufficient resources.
- Follow the implementation step: training, data collection, calculation, analysis, implementation and CIP.
- Consider the challenges: Strengthening employees’ willingness to change, insufficient data collection and complex production processes
Through careful planning and implementation, you can implement OEE in your company and sustainably increase your productivity and efficiency.
Use of technologies to improve OEE
The use of technology can play a crucial role in improving the OEE metric and thus optimizing overall equipment effectiveness.
The Role of Automation and Sensors
Automation and sensor technology can help improve availability, performance, and quality in production. They also enable accurate data collection and analysis, which consequently helps to identify and eliminate efficiency losses. By integrating automation solutions and sensors into production processes, companies can increase the OEE metric and increase productivity.
Examples of Technology Applications to Improve Overall Equipment Effectiveness
Some examples of the use of technologies to improve the OEE metric include:
- IoT (Internet of Things): IoT devices enable the monitoring and control of machines and systems in real time, thus improving their availability and performance.
- Predictive maintenance: Through the use of sensors and machine learning, companies can detect potential machine failures early and take preventive maintenance measures to reduce downtime accordingly.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI-powered systems can analyze production data and recognize patterns, which consequently help identify areas for improvement.
- Robot and cobot systems: The use of robots and collaborative robots (cobots) can increase efficiency and quality in production and thus contribute to the improvement of the OEE ratio.
New technologies and the future of OEE measurement
In the future, further technological innovations, such as big data, blockchain and augmented reality, could further revolutionize the measurement and analysis of overall equipment effectiveness. These technologies offer new possibilities for collecting, processing and analysing production data. As a result, there can be an even more accurate and effective improvement of the OEE ratio. The continuous development and integration of technologies into industrial processes will enable companies to increase their efficiency and also remain competitive.
Case Studies of Successful OEE Implementations
Case studies of successful implementations can provide valuable insights for companies looking to improve their own production. Here are some examples of successful implementations and the benefits that come with them:
Practice
- Automotive manufacturer: An automotive manufacturer has introduced the OEE indicator in its production lines and has thus been able to introduce targeted measures to improve availability, performance and quality. As a result, its Overall Equipment Effectiveness increased by 15%. This ultimately led to higher productivity and reduced production costs.
- Food producer: A food producer has reduced its downtime by 20% by implementing OEE and using sensors to monitor machinery and equipment. As a result, there was improved productivity and higher customer satisfaction.
- Electronics manufacturing: A company in the electronics industry reduced downtime in its production by 25% using OEE analysis and predictive maintenance strategies . This subsequently led to an increase in production capacity and also to an increase in the OEE ratio.
Lessons learned from successful implementations:
- Continuous improvement: A successful implementation requires a continuous improvement process that involves regularly analyzing data and taking action to increase the OEE metric.
- Employee engagement: Employee active participation and training is critical to success, as they are the ones who implement the improvement measures and influence the OEE metric.
- Use of technology: The use of technologies such as automation, sensors, and artificial intelligence can help improve the measurement and analysis of OEE and increase efficiency in production.
These insights can help companies successfully execute their own implementation and take advantage of the OEE metric.
Conclusion and recommendations for action
The implementation of OEE in industrial processes offers companies great advantages in terms of productivity, efficiency and also helps to save costs. Through the systematic analysis of the availability, performance and quality of production processes, weak points can then be identified and targeted improvement measures can be taken based on this. The use of technologies such as automation, sensors and artificial intelligence helps companies to optimize their OEE measurement and analysis.
The successful implementation of the OEE metric requires a high level of employee engagement and at the same time the use of technology. However, case studies show that companies in various industries can significantly increase their overall equipment effectiveness and benefit from the advantages. In order to keep a company competitive and continuously increase its efficiency, the implementation of OEE is relevant. As a result, the full potential of production processes is exploited and profitability is sustainably improved.
More about Overall Equipment Effectivness:
Niedersachsen | Hannover | Braunschweig | Oldenburg | Osnabrück | Göttingen | Celle | Lüneburg | Hamburg | Aurich | Leer | Diepholz | Hameln | Gifhorn | Cuxhaven | Uelzen | Emsland| Bremen |

