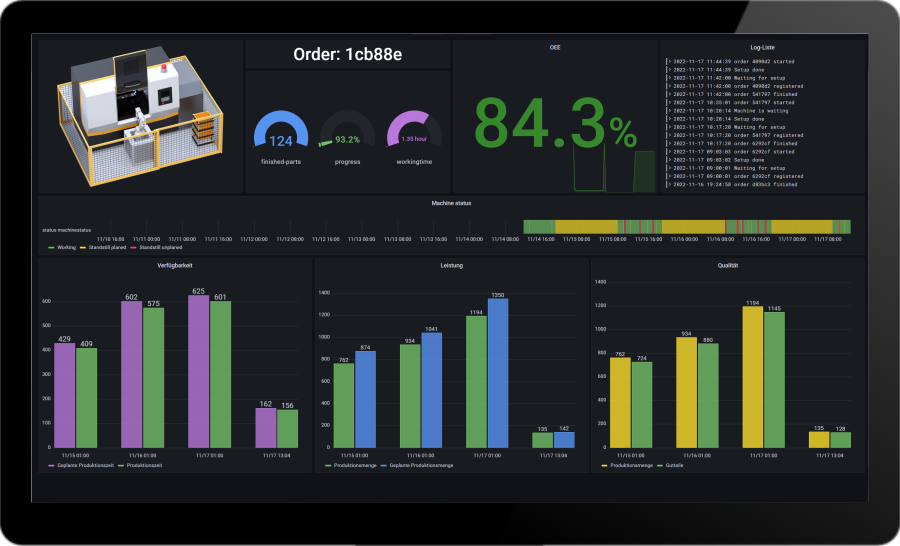
OEE definition – the overall efficiency of the machine
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a metric used in production to measure the efficiency of a machine or plant. The OEE definition describes the key figure with the three main components: availability, performance efficiency and quality rate. Each of these components has an impact on the overall efficiency of the machine or plant. A high OEE means that the machine or plant is operating effectively and meeting the specified performance targets.
Main components of OEE
Availability is the first component of OEE and describes how often the machine or equipment has been available and how often it has failed. This also includes planned downtime, such as maintenance or cleaning. High availability means that the machine or plant was ready for use for much of the production time.
Performance efficiency is the second component of OEE and describes how effectively the machine or plant works when it is available. These include, for example, the speed of the machine or the frequency of downtimes. High performance efficiency means that the machine or plant works effectively and has as little downtime as possible.
The quality rate is the third component of OEE and describes the quality of the products produced, measured by the number of defective products in relation to the total production. A high quality rate means that the machine or plant is working effectively and producing high-quality products.
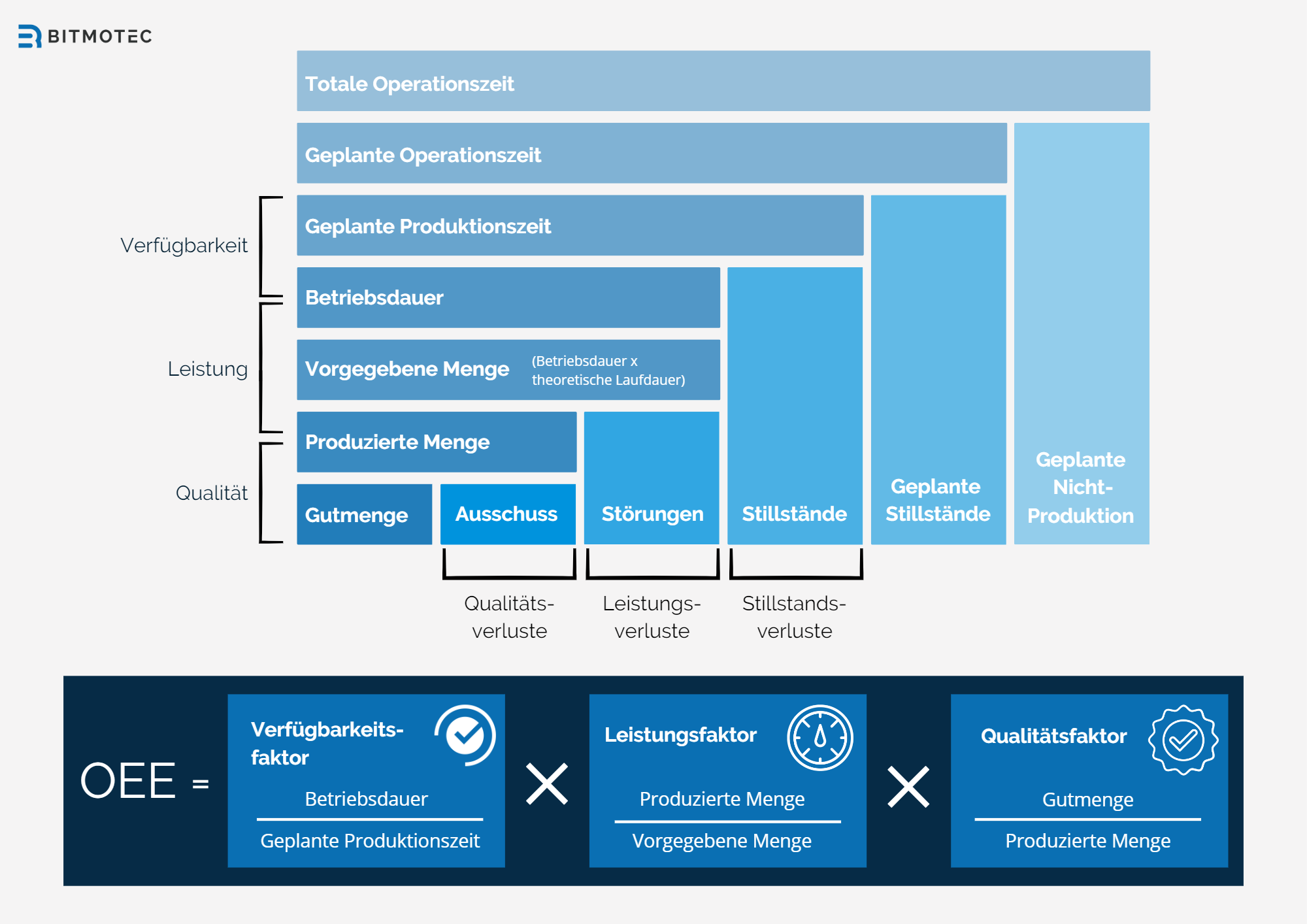
Calculation and interpretation
To calculate the key figure according to the OEE definition, these three components are multiplied together to give a value between 0 and 1, which is represented as a percentage. According to the OEE definition, a key figure of 100% means that the machine or equipment was available throughout the entire production period, with no downtime, with optimal performance efficiency and error-free production. An OEE of 0%, on the other hand, means that the machine or plant has been unavailable for the entire production period or that all products produced are faulty.
OEE Definition – Planned vs. Actual Production Time
An important aspect when calculating OEE is the distinction between planned and actual production time. Planned production time refers to the time you plan to produce your products on the existing machines, while actual production time is the time it took to produce. Discrepancies between these two times can affect availability and therefore OEE. If the actual production time is less than the planned time, it may be due to downtime that was not accounted for in the planning. On the other hand, a higher actual production time can lead to higher power efficiency and thus a higher OEE. It is therefore important to accurately record and monitor the planned and actual production time in order to correctly calculate the OEE key figure and identify areas for improvement.
Result
OEE is an important indicator of efficiency and productivity in production. Companies can use OEE to identify and optimize bottlenecks and weak points in production. A high OEE means higher productivity, lower costs and higher quality in production.
It is important that the data is collected and analyzed correctly in order to obtain a meaningful OEE. Companies should carry out regular OEE analyses in order to identify and react to changes in the efficiency of the machines or systems. The implementation of the OEE indicator in the industry can help to optimize processes and achieve higher efficiency and productivity.