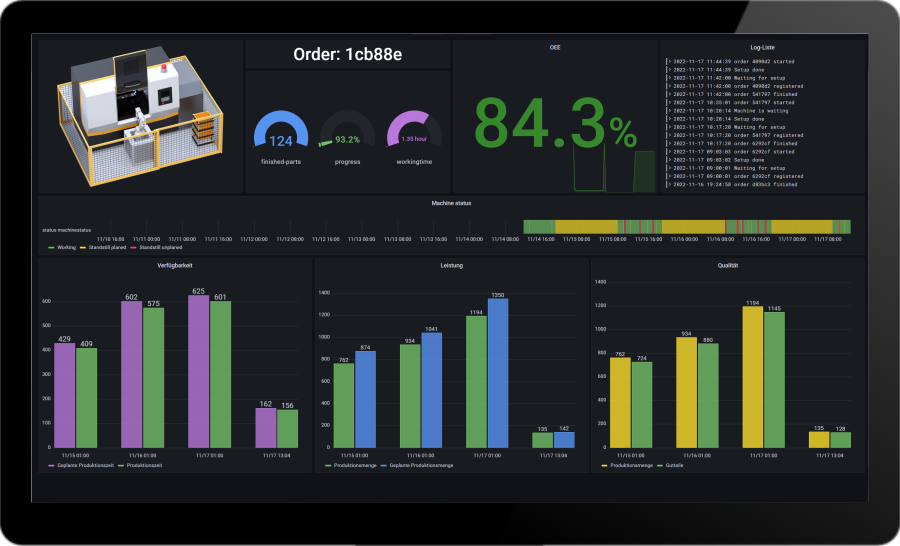
Machine availability and system availability
What is machine availability?
Machine availability and system availability are important key figures in production. Machine availability refers to the proportion of time that a particular machine is operational and can be used for production. Plant availability refers to the availability of all machines and systems in a production process. It indicates how much time the entire system can be used productively. Machine availability or plant availability is one of the main components of OEE. High machine and plant availability is crucial for efficient and successful production.
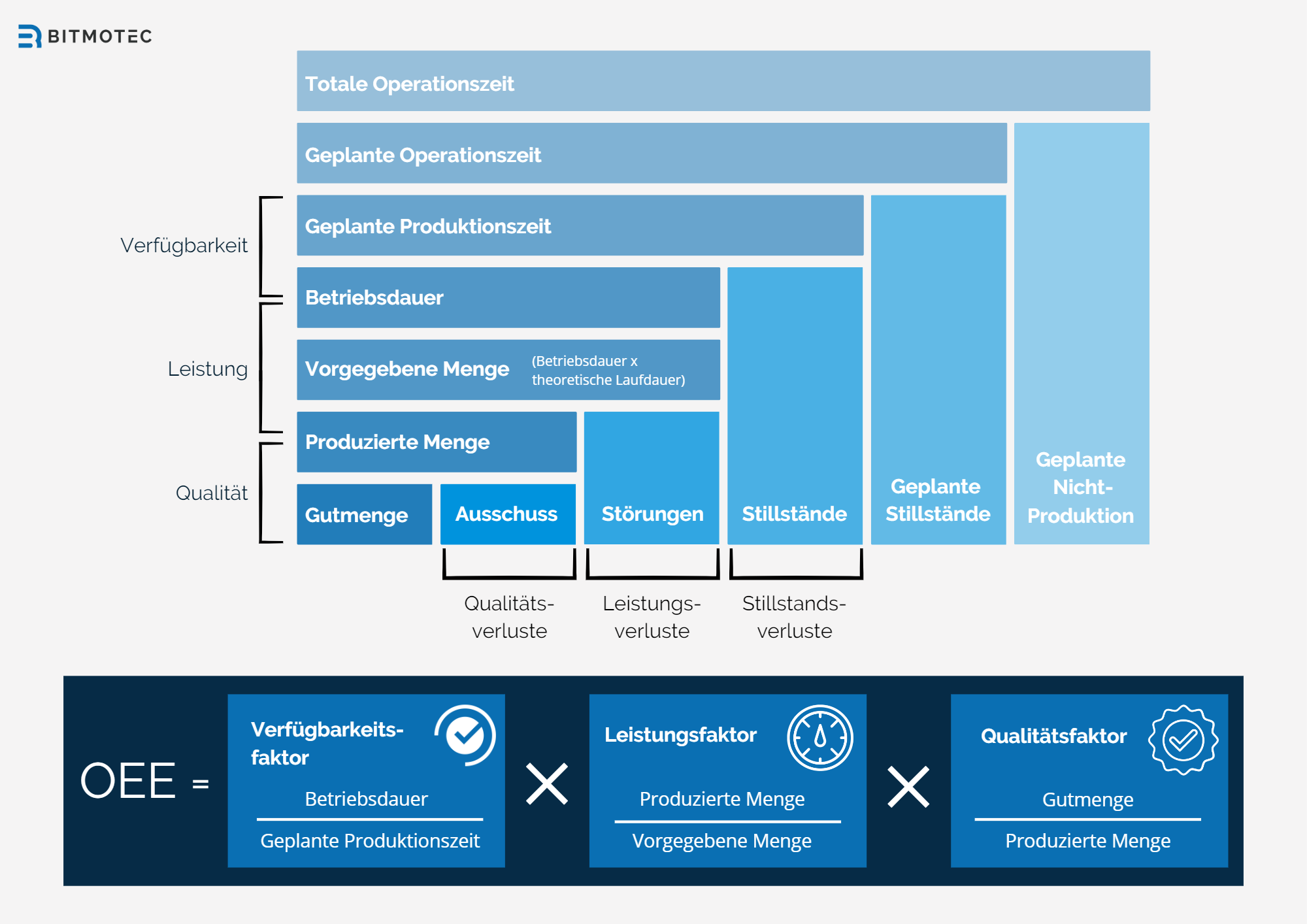
Calculation of machine availability
Machine availability or plant availability is usually expressed as a percentage and can be calculated using the following formula:
Machine Availability = (Planned Production Time – Downtime) / Planned Production Time x 100%
As an example, let’s assume that a production machine was available for 720 hours in a month, but was downtime for a total of 36 hours due to maintenance and repairs. The machine availability for that month would then be calculated as follows:
Machine availability = (720 – 36) / 720 x 100% = 95%
This means that the machine was able to be used 95% productively this month. High machine availability is an indicator of efficient and smooth production.
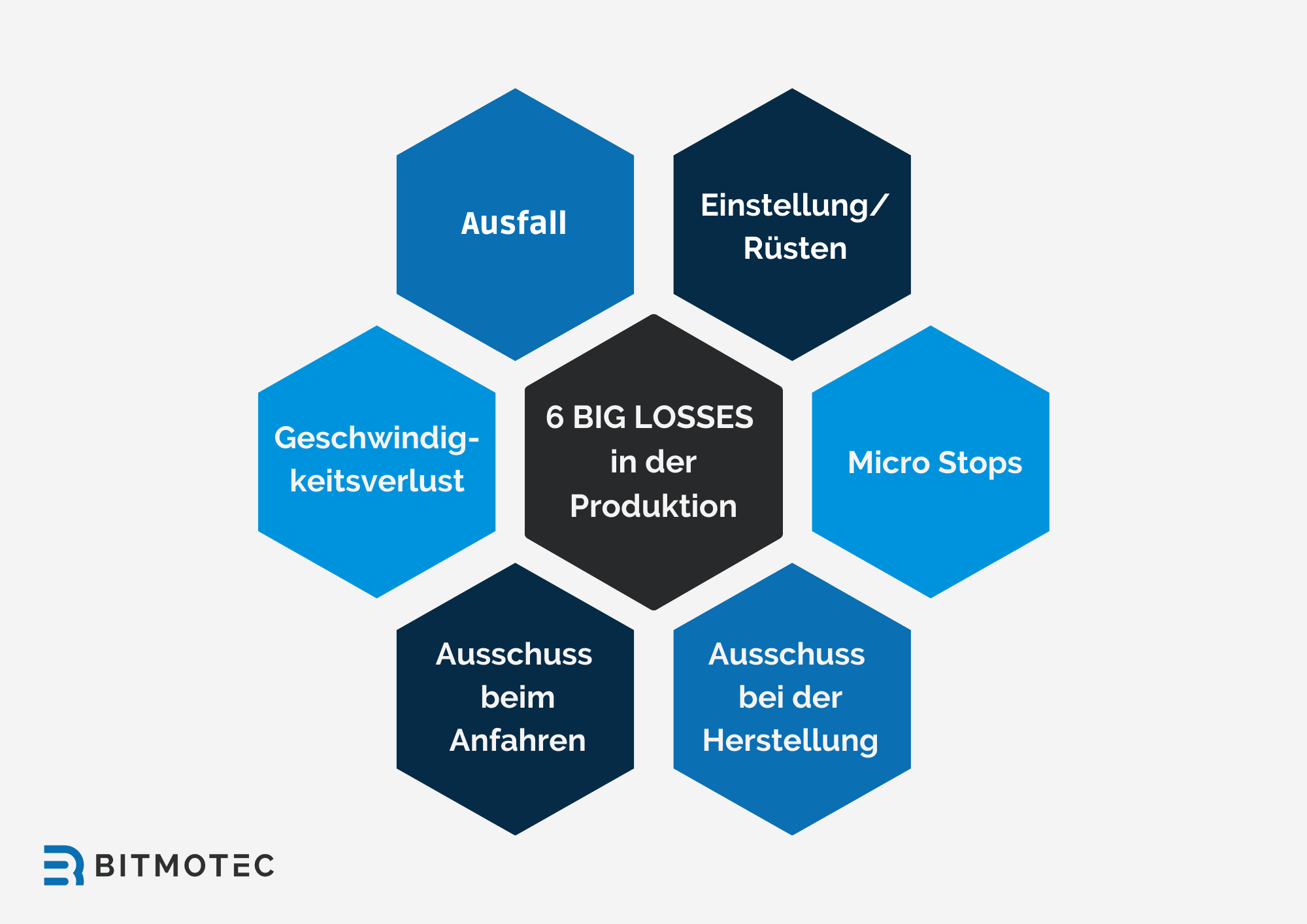
Loss of efficiency
There are various efficiency losses that can affect machine availability or plant availability. As a rule, eight important losses are distinguished. These include:
- Planned downtimes, e.g. for maintenance and cleaning
- Unplanned downtime due to machine breakdowns and repairs
- Set-up times needed to convert the machine to new products or orders
- Very small quantity losses caused by production downtime due to material shortages or inadequate planning
- Loss of speed due to inefficient work processes or non-optimal setting of the machine
- Loss of quality due to scrap and rework
- Bottlenecks in production due to machine downtime or production problems
- Personal efficiency losses due to absences, incapacity to work or inadequate training
The reduction of these losses is an essential factor in increasing machine availability or plant availability and thus the efficiency and profitability of production.
Improvement of machine and plant availability
There are various improvement measures to increase machine availability or plant availability. These include:
- Employee training
- Implementation of technologies such as monitoring systems
- Improvement of processes and workflows
- Implementation of preventive maintenance
- Use of replacement or rental machines during maintenance or repair.
The priority of the measures depends on the individual requirements and conditions of the production process. In general, preventive maintenance is one of the most important measures to avoid unforeseen machine breakdowns. However, implementing preventive maintenance requires careful planning and preparation, as well as certain prerequisites that a company must meet. These include:
- Data management: In order to successfully implement preventive maintenance, the relevant machine data must be systematically recorded and analyzed. This requires an appropriate IT infrastructure and effective data management.
- Knowledge of the machines: Employees should have a good understanding of the machines so that they can identify potential problems and take appropriate action. This may require employee training.
- Work planning: Preventive maintenance requires precise planning of maintenance and inspection work. Work planning must therefore be adjusted accordingly in order to integrate maintenance measures into the production process.
- Spare parts and tools: In order to carry out effective preventive maintenance, the necessary spare parts and tools must be available. This requires appropriate warehousing and good inventory control.
- Budget: The implementation of preventive maintenance requires an appropriate budget for the necessary investments in IT infrastructure, training, work planning and spare parts.
A successful implementation of preventive maintenance requires careful planning and a clear prioritization of the necessary measures. Companies should therefore conduct a thorough analysis of their needs before implementing preventive maintenance.