Industrial production
Introduction
Industrial production is a central pillar of the modern economy and plays a crucial role in the production of goods on a large scale. The term describes the process of processing raw materials and components in factories and production plants in order to subsequently produce finished products. Industrial production is characterized by the use of advanced technologies, automated machines, as well as efficient processes. This increases productivity and optimises the costs incurred. The spectrum of industrial production spans a wide range of industries. It can be found, for example, in in the automotive industry, electronics manufacturing and also food production. In doing so, it is largely responsible for meeting the needs of society while driving innovation. The following article on the topic of industrial production opens up a wide range of aspects. This is intended to shed light on the progress, challenges and significance of this fundamental sector for the modern world.
Definition of basic terms
The terms production, manufacturing and manufacturing are related to the industrial production of goods. Although they encompass similar concepts, they have slightly different meanings:
Production
The broad term “production” refers to the entire process of producing goods or services. This process can include several phases, e.g. starting with the planning and procurement of resources, through processing and assembly, to packaging and delivery of the finished products. Production includes all the activities required to produce a finished product. Consequently, this also includes the management of labour, machinery, materials and other resources.
Manufacturing
The term “manufacturing” refers directly to the manufacturing process of physical goods. It describes the by means of certain production methods and techniques. Conversion of raw materials or semi-finished products into finished products. Manufacturing can include mechanical, chemical or other processes that always aim to produce the final product according to the specified specifications and quality standards.
Production
The term “production” is also a synonym of the concept of “manufacturing” just presented and also refers to the process of producing goods as well as products. However, manufacturing can also have a broader meaning. This can also mean the design, development and planning of products as well as finally the production. So, the term encompasses the entire life cycle of a product, including conception, design, prototyping, manufacturing, and distribution.
Shortly
In summary, production, manufacturing, and manufacturing refer to various aspects of the industrial production of goods. Production encompasses the entire process of producing goods or services, while manufacturing and manufacturing are more specific to the transformation of raw materials into finished products and the life cycle of a product.

Production processes
Industrial production describes the use of various production processes. The following list gives an initial overview of the differences:
- Series production: Series production involves the production of products in large quantities, with production processes being largely standardized and automated. This allows for high efficiency and low unit costs.
- One-off production: In one-off production, on the other hand, it is possible to manufacture products according to individual customer requirements or in small quantities. Production is more flexible and less standardized, allowing it to respond to the specific needs of each customer.
- Mass production: Mass production is located between serial and one-off production and involves the production of a large number of similar products, where some variations are also possible.
- Assembly line manufacturing: Assembly line manufacturing is a continuous production process in which the product is transported along a conveyor belt through various production stations. In the course of the process, various specific work steps take place.
- Manual manufacturing: Manual manufacturing involves manual work processes in which the production of products is carried out by skilled workers without extensive automation.
- CNC Manufacturing: Computer-controlled numerical manufacturing (CNC) uses computer-controlled machines and tools to produce precise and complex products.
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing): Additive manufacturing uses layer-by-layer assembly processes to create three-dimensional objects from digital models.
- Casting: Casting processes are useful for pouring liquid materials into a mold to then form solid objects, such as metal casting or plastic injection molding.
- Forming processes: Forming processes use mechanical forces to deform the material and achieve a desired shape, e.g. by punching or bending metal sheets.
- Extrusion process: In extrusion, a material is pressed through a die to produce continuous profiles, tubes or hoses, for example.
- Sintering: Sintering is a process in which fine powders combine with each other under high pressure and temperature to produce solid components.
- Injection molding: Injection molding is a process of producing plastic parts in which molten plastic is injected into a mold, cooled there, and then solidified.
In short
This list provides an overview of various production processes that are used in industrial production. Through them, it is possible to adapt to the specific requirements of the respective industry and products, produce a wide variety of products.
Key production figures
Industrial production works with key figures that, for example, evaluate and improve the efficiency, performance and quality of manufacturing processes. The following are some of the key metrics:
- Production utilization: Production utilization measures the proportion of actual production capacity available. It provides information about the efficiency of production facilities and resources.
- Production throughput: Production throughput refers to the amount of finished products or units produced per unit of time. It is an indicator of the speed of production.
- Yield: Yield indicates how many products or units have been produced in a defect-free or acceptable quality ratio to total production.
- Scrap Rate: The scrap rate indicates how many products or units are discarded or considered scrap due to defects or defects during production.
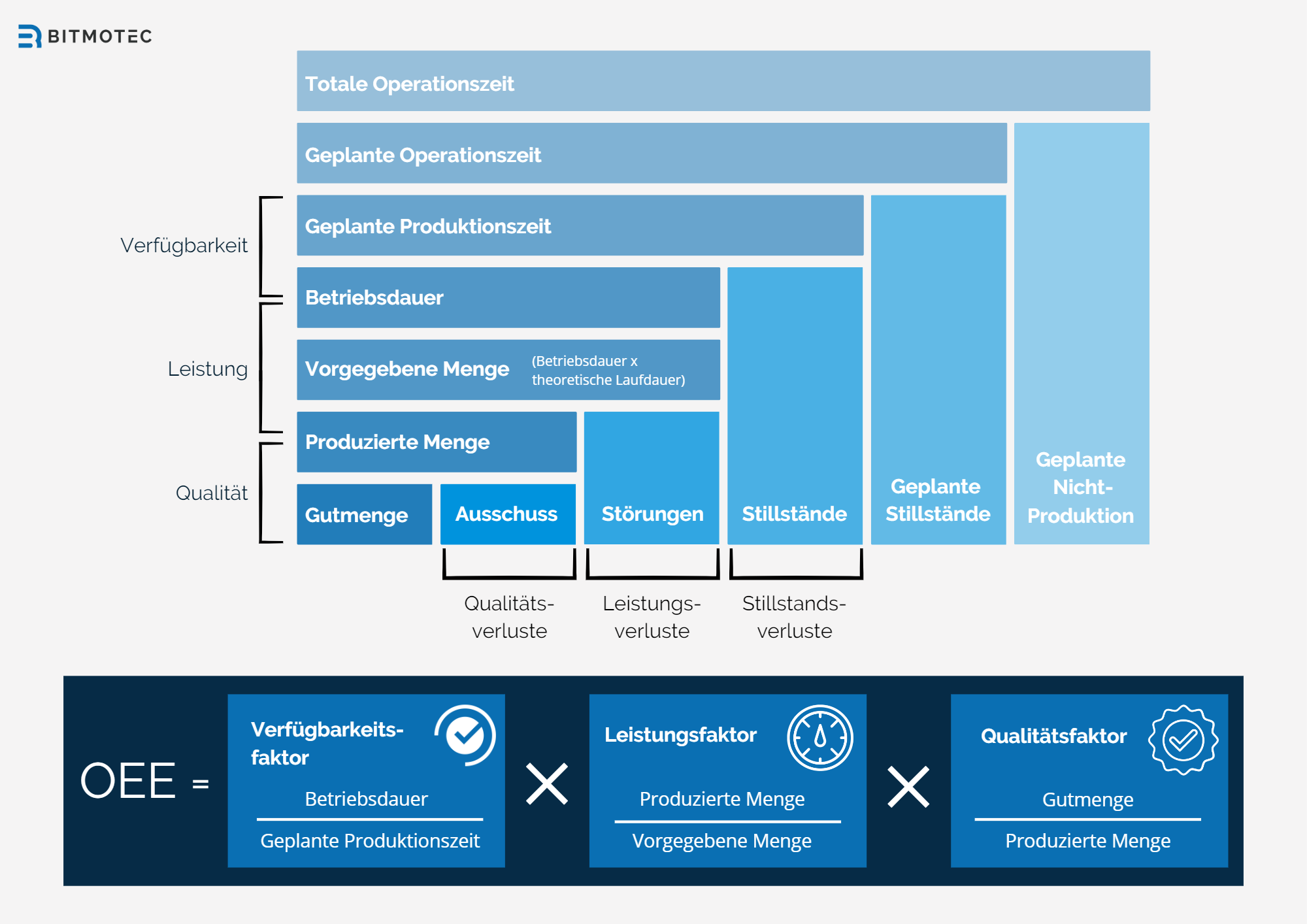
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): OEE is a metric that evaluates the efficiency of production equipment and takes into account the availability, performance, and quality of equipment (see figure).
- Lead time: Lead time measures the time it takes to manufacture a product from the beginning to the end of the production process. It affects delivery time and inventory.
- Inventory Turnover: The turnover rate indicates how often inventory is sold and replaced within a given period of time. It shows the efficiency of warehousing.
- Setup time: Setup time refers to the time it takes for a production plant or machine to retool another product.
- Machine availability: Machine availability measures the proportion of time that a production plant or machine is operational and not idle due to maintenance or breakdown.
- Energy consumption per unit: This metric measures the energy consumption per unit manufactured and provides information about the energy efficiency of production.
- Labor productivity: Labor productivity shows the amount or output produced per hour worked and is an indicator of labor efficiency.
- First Pass Yield: Initial yield measures the proportion of products or units produced on the first pass of the production process without rework or scrap.
In short
These metrics provide companies with critical information to monitor their production processes , identify bottlenecks, and make continuous improvements. Based on this, companies are able to steadily increase the efficiency and quality of industrial production.
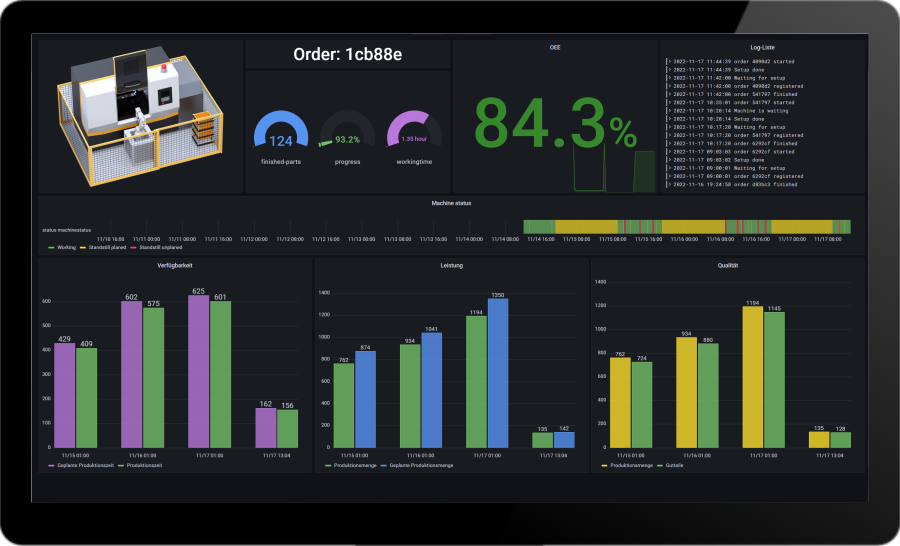
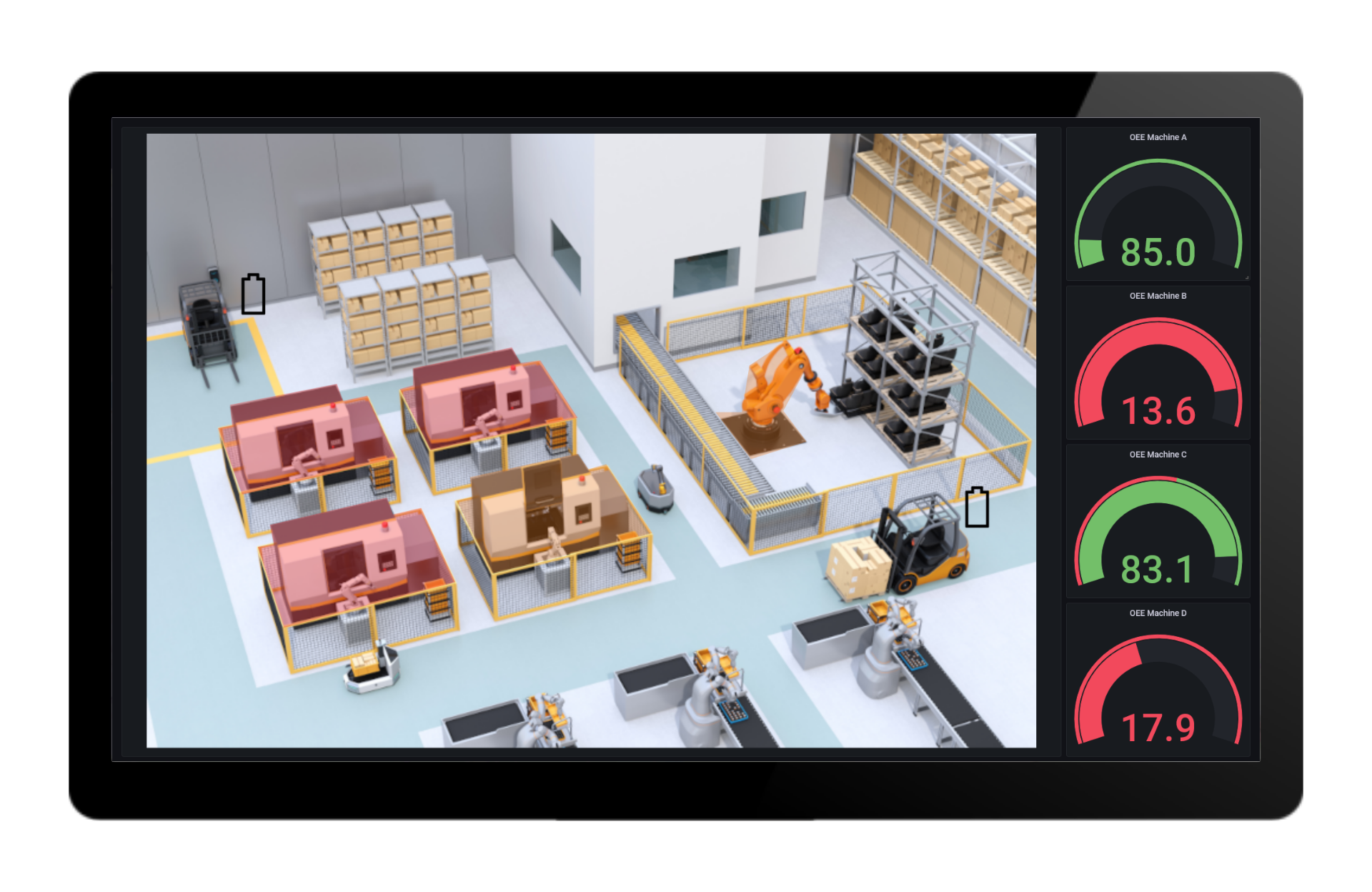
Production control station
A control room in industrial production is a central control room or command center. In this system, it is possible to consolidate, visualize and monitor all relevant information and data of the production process. The importance of a control center lies in the fact that it makes it possible to monitor, control and optimize the entire production process in real time. By integrating various automation and information systems, the control center provides a comprehensive view of the current condition of machines, equipment, stock levels and production performance.
The Benefits
The purpose of a control center is to ensure efficient production, to identify bottlenecks at an early stage, to coordinate production processes and to react flexibly to unforeseen events. As a result, production processes can be optimized, downtimes can be reduced and overall productivity can be increased. The control center thus plays a crucial role in supporting managers and employees to make data-based decisions and ensure smooth, transparent and efficient industrial production.
More on the topic:
Hannover | Niedersachsen | Oldenburg | Osnabrück | Göttingen | Celle | Lüneburg | Hameln | Aurich | Leer | Diepholz | Emsland | Gifhorn | Uelzen | Cuxhaven | Hamburg | Bremen | Braunschweig |