Condition Monitoring System
System Structure of Condition Monitoring Systems
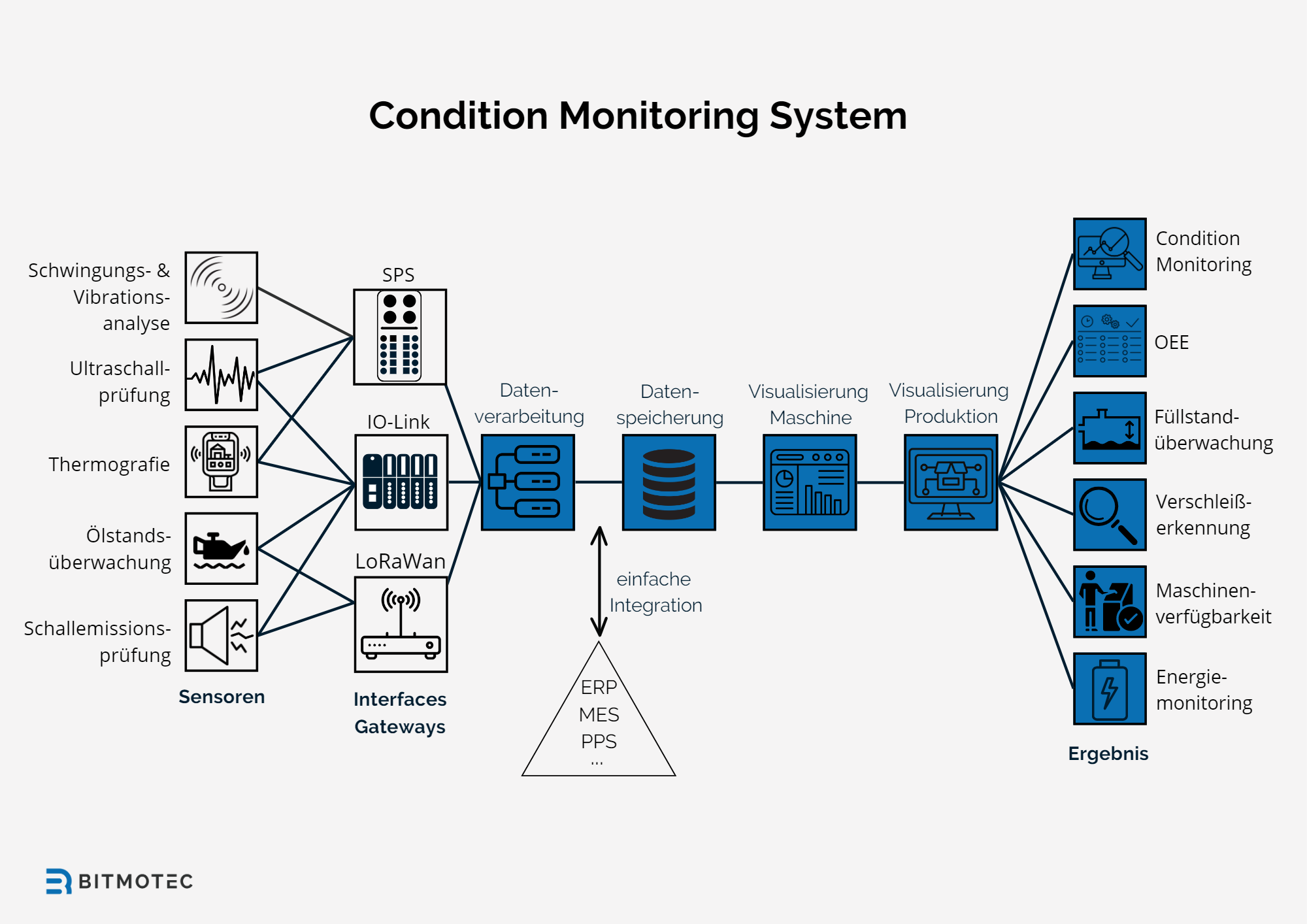
A typical condition monitoring system (CMS) consists of various components that work together to continuously monitor and evaluate machine conditions. The main components include:
- Sensors for recording machine data and environmental conditions
- Data processing unit (edge, server or cloud)
- Communication interfaces (wired or wireless) for data transmission
- Software for analysis, evaluation and visualization of data
- User interfaces for different user roles
Implementation and set-up process
- Planning and conception: In this phase, the requirements, goals and criteria are defined. This includes the selection of machines to be monitored, the identification of KPIs and the definition of measurement strategies.
- Sensors and data acquisition: The selected sensors are installed and configured on the machines. They continuously or periodically collect data on machine conditions and environmental conditions for the condition monitoring system.
- Data processing and analysis: The collected data is processed either locally (edge or server) or in the cloud. Modern analysis methods, such as machine learning, enable the detection of patterns, trends and anomalies in the condition monitoring system.
- Integration and Interfaces: The results of the data analysis are integrated into the existing IT infrastructure and forwarded to the responsible employees or systems via various interfaces (e.g. PLC, MES/ERP). This is done within the condition monitoring system.
- Visualization and User Interaction: The processed information is made available to machine operators, maintenance staff, production managers and maintenance managers via user interfaces. This enables efficient decision-making and predictive maintenance.
Sensors
Analogue sensor technology
Analog sensors are important components of many condition monitoring systems. They record physical quantities such as temperature, pressure or vibrations and convert them into analogue electrical signals. Analog sensors are usually inexpensive and offer high measurement accuracy. However, the transmission of analog signals can be susceptible to interference and signal loss, especially over long cable runs or in harsh industrial environments. Nevertheless, they remain an important part of sensor technology due to their reliability and ease of use.
Digital sensor technology (wired) using IO-Link as an example
Digital sensors convert the detected physical quantities directly into digital signals. A common wired communication technology is IO-Link, which provides a bidirectional point-to-point connection between sensors and controllers. IO-Link sensors offer advantages such as higher measurement accuracy, lower susceptibility to interference, simple parameterization and diagnostic options. However, they can be more expensive than analog sensors and require special IO-Link master modules to connect to controllers. Nevertheless, they are becoming increasingly important in condition monitoring systems due to their accuracy and integration into modern Industry 4.0 concepts.
Digital sensor technology (radio) using the example of LoRaWAN
Wireless sensors offer flexible and easy installation, especially for hard-to-reach machinery or large installations. LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is an example of a wireless technology designed specifically for IoT applications. LoRaWAN sensors enable energy-efficient and secure data transmission over long distances and are able to communicate through obstacles such as walls or machines. However, they can result in higher costs and greater complexity in network planning. Nevertheless, they are a valuable component of modern condition monitoring systems due to their flexibility and scalability.
Measurement Strategies
Measurement periods of condition monitoring
The measurement periods in a condition monitoring system can vary depending on the requirements and goals of the system. There are three main categories of measurement periods:
- Continuous Measurement: This enables real-time analysis and response to machine conditions. This makes it ideal for critical installations where a quick response to problems is required.
- Periodic measurement: The Condition Monitoring System takes measurements at regular intervals. This allows for sufficient monitoring without unnecessarily increasing energy consumption or the amount of data.
- Ad-hoc measurement: Measurements if required, e.g. if a specific fault is suspected or to check on a repair.
Measuring points (type and location)
The selection of measurement points is crucial for effectiveness. There are two aspects to consider:
- Type of measuring points: The type of measurement points refers to the different physical quantities to be measured, such as temperature, vibration, pressure or sound. The selection of measurement points depends on the specific requirements and goals of the condition monitoring system.
- Location of measuring points: The location of the measuring points refers to the positioning of the sensors on the machines or systems. Careful planning is required to ensure that the sensors are positioned in the optimal locations. Subsequently, it is possible for companies to provide meaningful and reliable data for the condition monitoring system.
Integration options into the IT structure
On-premises (Edge) – On-premises (Server) – Cloud
With edge integration, the data from the condition monitoring system is processed directly on the machine or system. Edge devices are able to process data in real-time and make decisions without relying on central servers or cloud resources. This can lead to faster response times and better network utilization. However, local data processing can limit scalability and result in higher hardware costs.
Local server integration makes it possible to process and store production data within the corporate network. This provides the benefit of better control over the data and reduces latency. However, there may be higher costs for IT infrastructure and ongoing operations, as well as the need for regular maintenance and updating of server systems.
Cloud integration provides a central platform for storing, processing, and analyzing machine data. This allows for high scalability, flexibility, and easy integration with other cloud-based services, such as machine learning or artificial intelligence. However, cloud integration can raise privacy and security concerns, and you may experience latency or dependencies on the internet connection.
Comparison – Pros and Cons of Integration Options
Each integration option for a condition monitoring system has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Edge Integration: Advantages include faster response times and reduced network load, while the disadvantages are limited scalability and higher hardware costs.
- Local Server Integration: Advantages include better control over the data and lower latency, while the disadvantages are higher IT infrastructure costs and maintenance.
- Cloud Integration: Advantages are high scalability and flexibility, while the disadvantages are privacy and security concerns, as well as possible latency or dependencies on the internet connection.
Interfaces
Machine Operator / Maintenance Employee (User Interface)
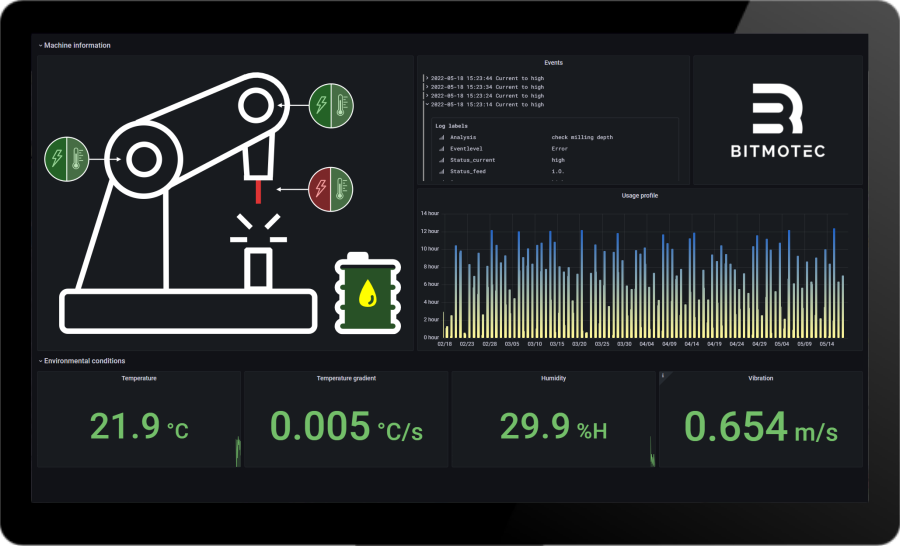
An effective condition monitoring system should have a user-friendly interface that allows machine operators and maintenance staff to easily monitor the condition of the machines and equipment. This interface should provide both easy-to-understand information and detailed analytics and diagnostics to help users respond quickly to issues and make proactive maintenance decisions.
Production Manager / Maintenance Manager (User Interface)
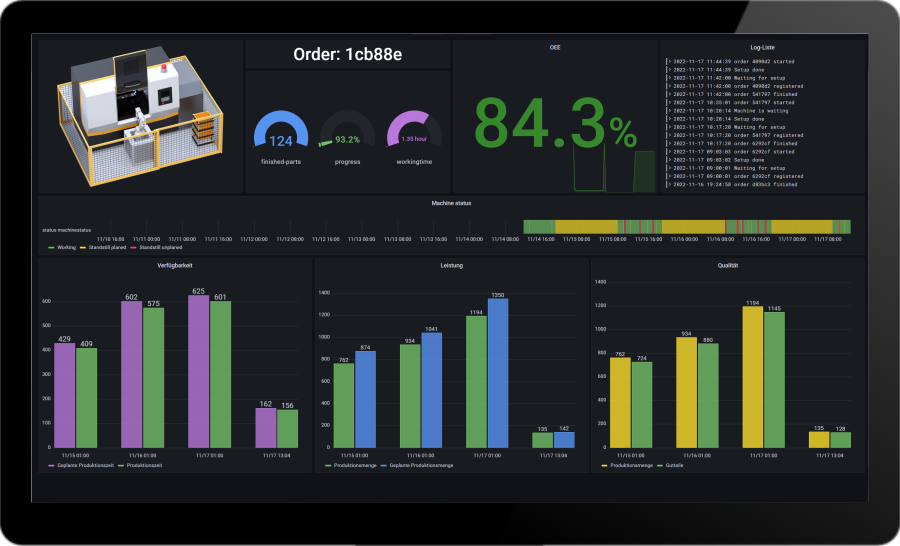
It is important for production and maintenance managers to have access to a condition monitoring system that provides them with a comprehensive overview of the condition of all machines and equipment in the production process. The interface should be tailored to the needs of these decision-makers, allowing them to review and manage performance indicators, maintenance schedules, and other relevant information at a glance.
PLC
The connection of a condition monitoring system to the programmable logic controller (PLC) is crucial to obtain real-time data on the operation of the machines and systems. Seamless integration of the PLC allows for greater control and responsiveness in the processing of condition data and the control of maintenance actions.
MES / ERP
Integrating a condition monitoring system with a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is critical to the effective use of condition data across the organization. Such integration makes it possible to make O&M decisions based on real-time data, while optimizing the flow of information between different departments and systems.
Current trends
IIoT as an important factor for condition monitoring systems
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) plays a crucial role in the development and improvement of condition monitoring systems. By connecting machines, systems and sensors within the IIoT, comprehensive and up-to-date information about the condition and performance of equipment can be collected. This allows for better decisions and leads to more efficient and effective maintenance. Linking condition monitoring systems to IIoT platforms also allows for the integration of data from different sources and the sharing of information between different locations and departments within an organization.
New technologies
The rapid development of new technologies and products has led to condition monitoring systems becoming more and more powerful and versatile. Examples include advanced sensors that enable more precise measurements, machine learning and artificial intelligence, which play an important role in the analysis and interpretation of condition data, and innovative communication protocols and infrastructures that simplify the exchange of information between machines and systems. In addition, new IIoT-based technologies such as edge computing and digital twins are fueling development by enabling real-time analytics and simulations to monitor asset health even more accurately and efficiently.
The integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) into condition monitoring systems opens up new possibilities for the maintenance and training of maintenance personnel. With AR and VR technologies, maintenance teams can visualize asset conditions and receive detailed, step-by-step guidance to perform maintenance more effectively and safely.

Applications
Machine Availability in the Context of OEE
Improving machine availabilityis a key application for condition monitoring systems. Continuous monitoring of machines and equipment can reduce unplanned downtime and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). In addition, monitoring helps to ensure that maintenance work can be carried out in a targeted and efficient manner, which increases machine availability and increases production output.
Energy monitoring in production
Energy efficiency is another important area of application. By monitoring the energy consumption of machines and equipment, companies can optimize their energy consumption and thereby reduce operating costs. Condition monitoring systems make it possible to detect energy losses at an early stage and initiate countermeasures to increase energy efficiency.
Maintenance monitoring for machine tools
Condition monitoring systems also play a crucial role in the maintenance monitoring of machine tools. Thanks to the continuous recording of operating data and wear indicators, maintenance intervals can be precisely planned and optimized. This results in a longer tool life, higher production quality and a reduction in maintenance costs.
Monitoring of technical building equipment (TGA)
The monitoring of technical building equipment (TGA), such as heating, ventilation and air conditioning technology, is another area of application. By continuously collecting operating data and condition information, building operators can optimize the efficiency of their systems, reduce energy consumption and extend the service life of technical equipment.
